- Albanian
- Arabic
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Czech
- English
- French
- German
- Hebrew
- Hungarian
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- kazakh
- Persian
- Russian
- Thai
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
Explore Roller Coaster Classifications & Ride Types | Manufacturer Guide
Roller coaster classifications form the backbone of the global amusement ride industry, guiding everything from theme park ride designs to regulatory compliance, manufacturing standards, and user experience expectations. With rapid advancements in roller coaster graph equations, ride engineering, and the growing diversity of types of roller coaster rides, understanding these classifications is crucial for operators, manufacturers, and enthusiasts alike. This article, created by the industry-leading manufacturer Hebei Zhipao Amusement Equipment Manufacturing Co.LTD., will provide a meticulous overview of all major aspects related to roller coaster engineering, design parameters, types, manufacturers, technical trends, and more.
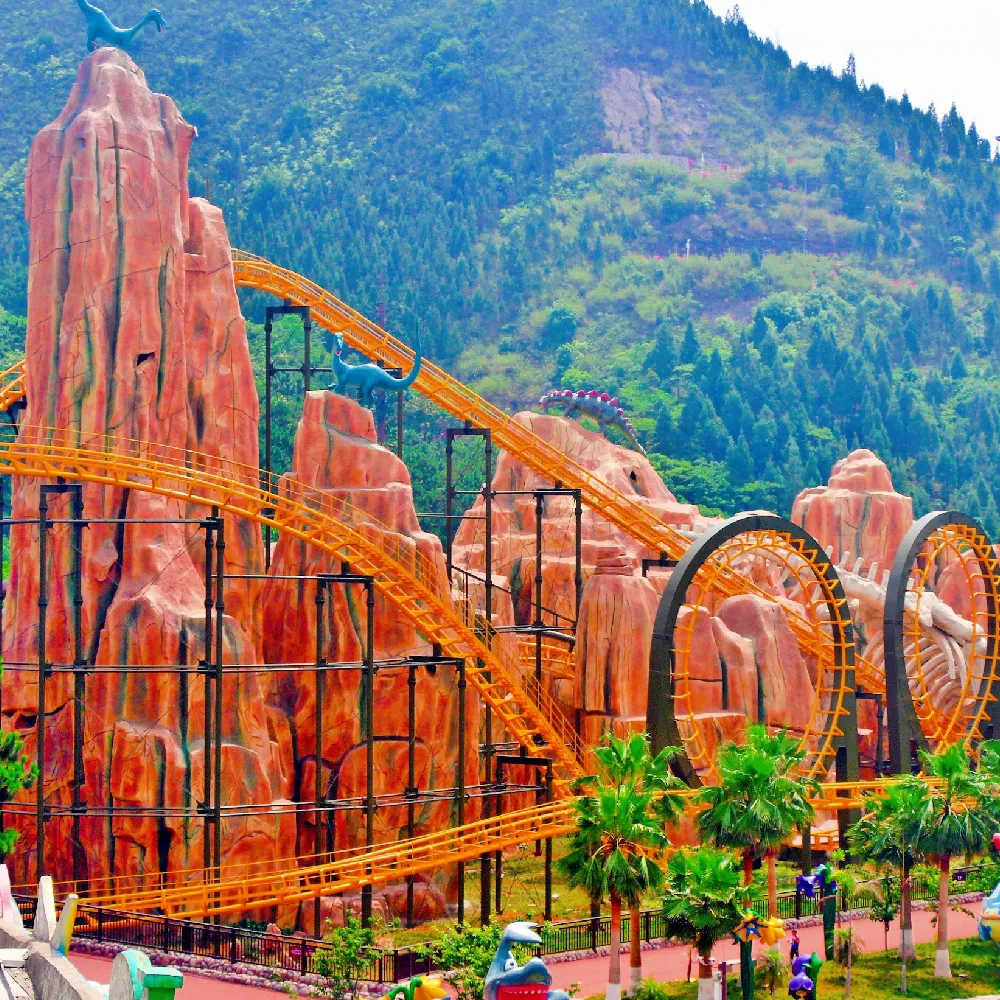

Industry Overview: The Evolving Landscape of Roller Coaster Classifications
As amusement parks worldwide aim to attract greater footfall and offer unique experiences, the role of roller coaster classifications has expanded beyond simple ride types. Today, rides are classified according to technical specifications (track layout, speed, degree of inversion, materials), ride dynamics (steel, wooden, launched, inverted, suspended, spinning, etc.), capacity, safety systems, and intended user groups. Notably, China has surged as a major center of roller coasters manufacturers, providing cutting-edge rides globally.
Famous industry events and forums such as IAAPA (International Association of Amusement Parks and Attractions) continuously discuss evolving classification standards and their impact on roller coaster manufacturers and park operators (IAAPA Community).
Official Website
As one of China's leading rollercoaster manufacturers and theme park ride manufacturers, we specialize in design, development, and production of modern amusement rides—including large-scale steel coasters. Certified to international quality standards, Zhipao delivers turn-key solutions for parks across Asia, Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
Phone: +8603195235000
Mobile: +8613231954678
Email: 370459358@qq.com
Address: No.2969 Xiangdu South Road, Xiangdu District, Xingtai City, Hebei Province, China
1. Defining Roller Coaster Classifications & Associated Terminology
Rides are traditionally categorized by construction, driving principles, passenger orientation, and special features. Below is a reference table summarizing the most recognized roller coaster classifications worldwide:
| Classification | Sub-types | Construction Material | Drive/Launch System | Main Features | Popular Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Roller Coaster | Inverted, Floorless, Hyper, Giga | Steel | Chain-lift, LSM, LIM, Hydraulic Launch | High speed, smooth, loops, inversions | Intamin Giga, B&M Inverted |
| Wooden Roller Coaster | Duel-tracked, Out-and-back | Wood w/ metal rails | Chain-lift, Gravity | Traditional, airtime hills, rougher ride | The Beast, El Toro |
| Launched Coaster | LSM, LIM, Hydraulic Launch | Steel or Hybrid | Magnetic, Hydraulic, Pneumatic | Immediate acceleration, no lift hill | KINGDA KA, Xcelerator |
| Suspended/Inverted | Suspended, Inverted, Wing | Steel | Chain-lift | Passengers below/around track | Nemesis, Batman: The Ride |
| Spinning Coaster | Free spin, Controlled spin | Steel | Chain-lift | Rotating cars, unpredictable forces | Time Traveler |
| Mine Train | Family, Themed | Steel | Chain-lift | Scenic, themed, mild thrills | Big Thunder Mountain |
| Hybrid Coaster | Steel track/Wooden structure | Wood & Steel | Chain-lift | Smooth with classic feel | Steel Vengeance |
These roller coaster classifications influence everything from investment choices to marketing strategies, and underpin the design improvements found in the latest roller coasters from leading rollercoaster manufacturers in China and worldwide (CoasterForce Forum).
2. Technical Trend Visualization: Roller Coaster Classifications Parameters
3. Product Focus: Four Loops Roller Coaster (Zhipao’s Flagship Innovation)
Key Specs:
- Track Length: 480m
- Track highest point: 25.2m
- Cabin quantity: 4
- Number of passengers: 16 persons
- Fastest running speed: 69KM/h
- Total power: 90kW
- Site area needed: 90m × 40m
- Running time per cycle: ≈100 seconds
4. Application Scenarios & Industry Trends
- Theme Parks: The main stage for every roller coaster manufacturer, parks demand ever more thrilling, reliable, and efficient rides. Four Loops Roller Coaster delivers with compact footprint and intense inversions.
- Urban Entertainment Centers: Space-efficient rides (Four Loops needs only 90m x 40m) are preferred in dense cities, fueling demand among developers in China, UAE, and Singapore.
- Research Facilities: Utilizing advanced roller coaster graph equations to optimize ride forces, improve safety margins, and enhance material utilization for steel/wooden structures.
- Tourism Development: Unique types of roller coaster rides (i.e., spinning, hybrid, launched) are leveraged as flagship attractions in tourist destinations worldwide.
- VR-integrated Coasters: Manufacturers have begun integrating VR and AR, requiring new safety and classification parameters as per emerging standards (reference).
5. Roller Coaster Graph Equations in Modern Ride Engineering
Optimization of ride layouts and force profiles increasingly relies on mathematical roller coaster graph equations, which define track curvature, acceleration, and g-forces. Example formulae widely used by top theme park ride manufacturers include:
- Cubic Hermite spline interpolation: For smooth track transitions; ensures continuous derivative and no abrupt g-forces (IEEE Paper).
- Clothoid (Euler spiral): For loop and inversion entries—minimizes jerk, maximizes rider comfort.
- Second-order ODEs: Used in advanced simulation of cart dynamics, especially in multi-inversion layouts like Four Loops Roller Coaster.
The latest model improvements by Hebei Zhipao Amusement Equipment Manufacturing Co.LTD. leverage these equations in both design and in quality control simulations, ensuring operational safety and an optimal ride experience as proven in roller coaster classifications of our flagship products.
6. Overview of Roller Coasters Manufacturers (China & Global)
- China: Leading the world in production volume and engineering. Notable players: Hebei Zhipao Amusement Equipment Manufacturing Co.LTD. (Zhipao), Golden Horse, Jinma Rides.
- Europe: Intamin, Mack Rides, Vekoma.
- USA: Bolliger & Mabillard (B&M), Premier Rides, Gravity Group.
- Japan: Sansei Technologies, Senyo Kogyo.
- Emerging: New entrants from UAE and India focusing on compact city-centric solutions.
Zhipao's Four Loops Roller Coaster stands out due to its balance of height, speed, advanced safety, space efficiency, and customized theming options—favored by both domestic and international park operators.
7. Multimedia: Roller Coasters Video & Immersive Technology
Modern roller coasters video integration is not simply for record or marketing—POV videos are used by engineering teams to validate track smoothness, gauge user reactions, and propose upgrades. For ride designers, virtual simulations, and 3D animated walkthroughs are essential pre-production tools.
8. Professional Q&A: Industry-Specific Key Topics (EEAT)
-
Q1: Which primary material is chosen for modern looping coasters and why?
A: High-tensile structural steel is used due to its superior yield strength, weldability, and anti-fatigue properties, crucial for withstanding the dynamic loads experienced in multi-inversion rides. -
Q2: What calculation software is used for roller coaster graph equations?
A: Most major roller coaster manufacturers employ Autodesk Inventor, CATIA, and custom MATLAB modules for dynamic simulation, force mapping, and 3D track optimization. -
Q3: How are passenger safety standards harmonized internationally?
A: Adherence to EN 13814 (Europe), ASTM F2291 (USA), and updated Chinese GB/T standards ensures global reliability; Zhipao is fully certified to these. -
Q4: What's the typical installation timeline for a 4-loop steel coaster?
A: Average timeline ranges from 6 to 9 months, depending on site conditions, logistics, and theming requirements. Complex modularization by Zhipao can reduce this by 20%. -
Q5: What passenger harness is used for Four Loops Roller Coaster?
A: Zhipao utilizes redundant hydraulic over-the-shoulder restraints and seat belt backup, validated in both TÜV and China National safety reviews. -
Q6: What maintenance schedule should be followed?
A: Daily ride tests, weekly NDT (non-destructive testing) of structural welds, plus quarterly track alignment measurements are industry best-practice—services provided with all Zhipao installations. -
Q7: How are ride forces analyzed to ensure comfort and safety?
A: Full-ride lateral and vertical G-profiles are plotted using FEA (finite element analysis) based on carefully constructed roller coaster graph equations, with limits set to ≤4.5g (positive) and ≥-1.2g (negative) per relevant standards.
9. Why Choose Hebei Zhipao Amusement Equipment Manufacturing Co.LTD.?
- Decades of proven expertise in large-scale roller coaster classifications engineering and manufacturing.
- International safety certification & proprietary simulation tools ensure ride reliability and innovation.
- Experience with all major ride types: from classic wooden and steel to ultra-modern launched, inverted, hybrid, and spinning models.
- Strong after-sales support including installation, training, and global maintenance services.
- Custom design based on park theme and required technical specs.
Phone: +8603195235000 | Mobile: +8613231954678
Email: 370459358@qq.com
Official Website »
10. Conclusion & Further Resources (EEAT References)
The evolution of roller coaster classifications is a testament to industry innovation and growing global demand. Modern rides like the Four Loops Roller Coaster, engineered and manufactured with excellence by Hebei Zhipao Amusement Equipment Manufacturing Co.LTD., exemplify the synergy of proven engineering, advanced design, and international cooperation.
Further reading & references:
- IAAPA Industry Forum: Roller Coaster Safety & Design (2024)
- ScienceDirect: Roller coaster track curve optimization using graph equations
- CoasterForce Forum: Types of Roller Coaster Rides
- Roller Coaster Database (RCDB): Global Ride Classifications & Stats
-
Top-Quality Used Amusement Park Rides & Equipment – Great Deals!Jul.22,2025
-
Custom Roller Coaster Sets | Build 736-Piece Models with FunctionsJul.21,2025
-
Four Loops Roller Coaster - Ultimate Thrill Ride | Book AdventureJul.21,2025
-
City Ferris Wheel – Experience the Ultimate Ride with City Star Ferris Wheel ThrillJul.08,2025
-
Explore All Types of Roller Coasters Find the Best Rides for Every Thrill SeekerJul.08,2025